Climate Change
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Climate change includes both global warming driven by human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases and the resulting large-scale shifts in weather patterns. Though there have been previous periods of climatic change, since the mid-20th century humans have had an unprecedented impact on Earth's climate system and caused change on a global scale.
What is climate change?
Climate change is generally defined as a significant variation of average weather conditions -say, conditions becoming warmer, wetter, or drier over several decades or more. It's the longer-term trend that differentiates climate change from natural weather variability.
Record floods, Raging storms, Deadly heat, Climate change manifests itself in myriad ways and is experienced by every living being, although not equally.
What will climate change means?
People
Climate change will transform the way we live, causing water shortages and making it harder to produce food.
Some regions could become dangerously hot and others uninhabitable because of rising sea levels. Extreme weather events like heatwaves, downpours, and storms will become more frequent and intense, threatening lives and livelihoods. People in poorer countries, which are least able to adapt, will suffer most.
Environment
Polar ice and glacier are melting fast with low-lying coastal areas threatened with flooding by rising seas.
As permafrost frozen ground melts in places like Siberia, methane another greenhouse gas will be released into the atmosphere, worsening climate change. The weather conditions needed for wildfires are becoming more likely.
Nature
As their habitats change, some species will be able to move to new locations. But climate change is happening so rapidly many are likely to become extinct. Polar bears are at risk of disappearing as the ice they rely on melts away.
Atlantic salmon could be devastated as the river waters in which they breed warm up. Tropical coral reefs may disappear as oceans absorb CO2 and become more acidic.
What are the causes?
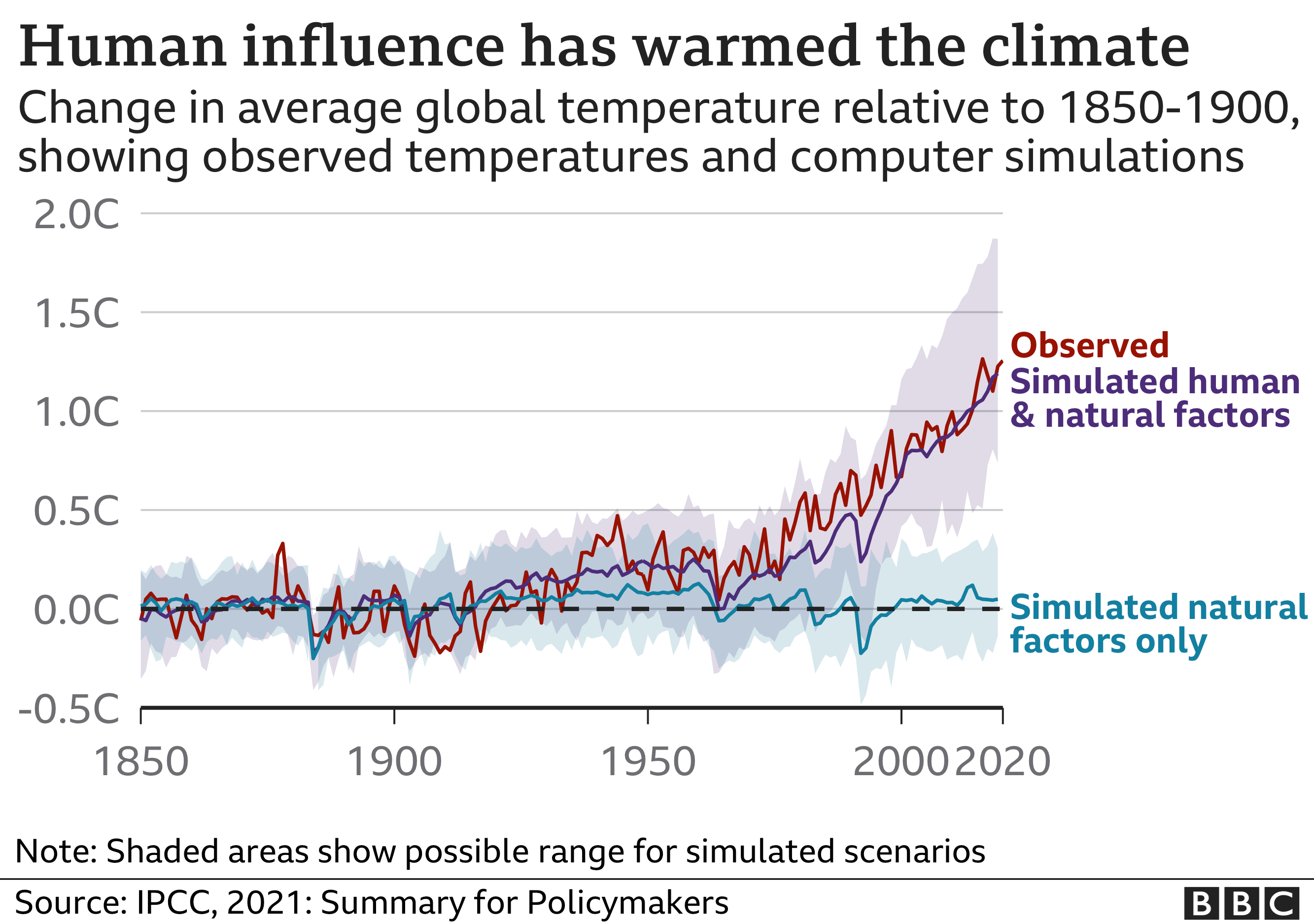
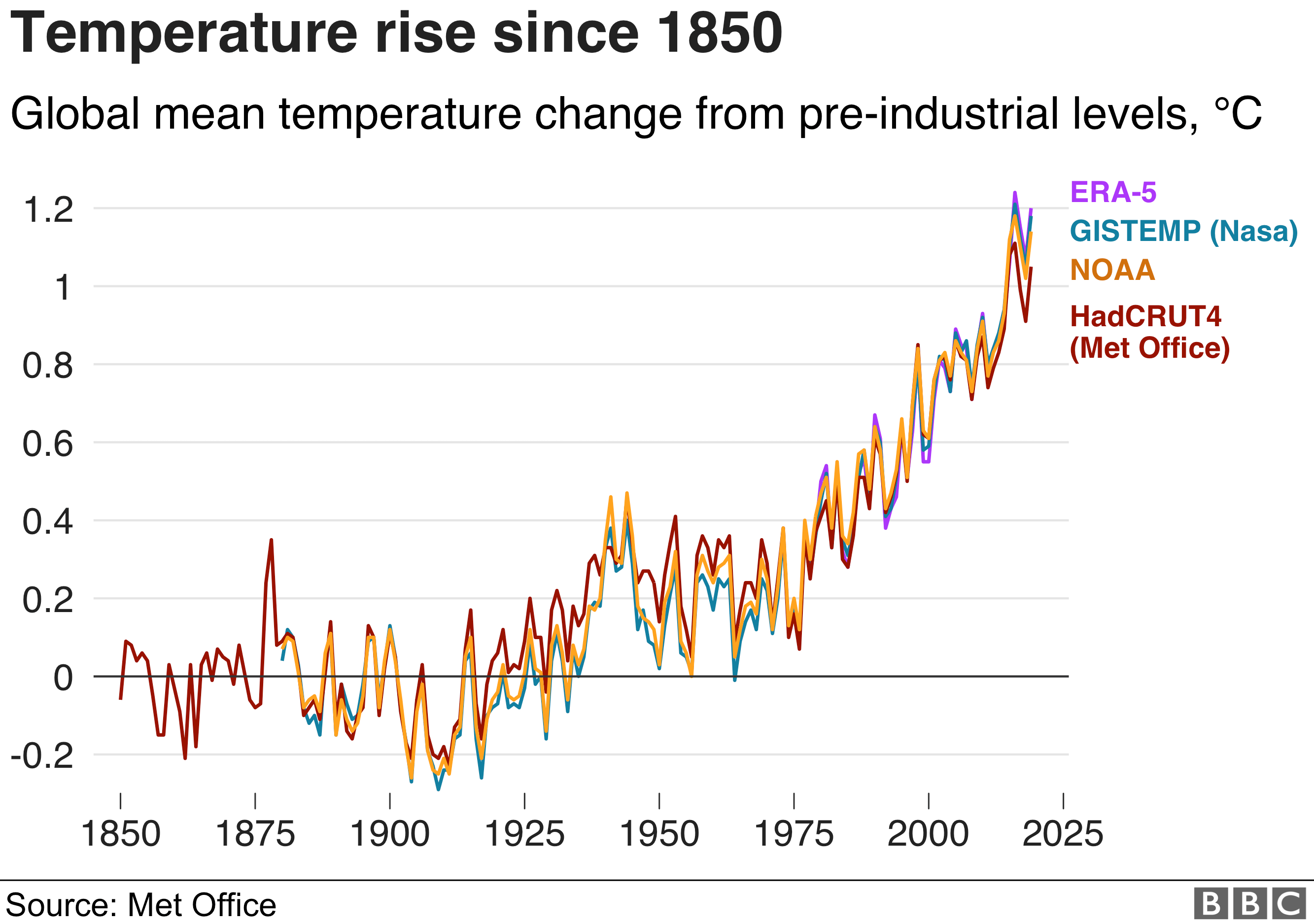
There have always been natural variations in the climate. But global temperatures are rising now because of human activities. The world is about 1.2C warmer than before people started using oil, gas and coal to power factories and transport, and to heat homes.
The greenhouse gases released by burning these fossil fuels trap the Sun's energy.
The amount of one greenhouse gas in the atmosphere CO2 has risen about 50% since the 19th century and 12% in the past two decades. Another source of greenhouse gases is deforestation.
When trees are burned or chopped down, the carbon they normally store is released.
What will happen in the future?
Scientists have set a temperature increase of 1.5C as the 'safe' limit for global warming. If temperature goes higher, damaging changes to the natural environment will probably transform humans way of life.
Many scientists believe this will happen and predict rises of 3C or more by the end of the century. The effects vary around the world:
- The UK will be vulnerable to flooding caused by extreme rainfall.
- Low-lying island nations in areas such as the pacific region could disappear under rising seas.
- Many African nations are likely to suffer drought and food shortages.
- In North America, worsening drought conditions are likely to hit the western US, while other areas will probably see increased rainfall and more intense storms.
- Australia is likely to suffer extremes of heat and drought.
- reduce their reliance on cars by taking public transport or cycling.
- insulate their homes
- take fewer flights
- eat less meat and dairy
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments
Post a Comment